elisa test lab|elisa test explained : import ELISA is an abbreviation for "enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay." In 1974, P. Perlmann and E. Engvall developed the test as a substitute for certain radioimmunoassay tests, and eventually, it replaced the western blot test for . Parker Autoclave Engineers repair and refurbishment services provide a cost effective means of keeping your existing high pressure equipment in optimum condition. These services are .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Please provide adequate ventilation for heat and steam capture around the sterilizer. Inadequate ventilation may interfere with facility fire detection and suppression equipment.Grâce à son traitement par autoclave, ce piquet en bois de pin peut résister aux différentes agressions. Les insectes, les intempéries ou les champignons sont souvent .
top 10 elisa tests
test for hamstring tear
reasons for positive elisa tests
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also called ELISA or EIA, is a test that detects and measures antibodies in your blood. This test . An ELISA test is a blood test that looks for antibodies in your bloodstream. When certain antibodies are present, it’s a sign your immune system is trying to fight off a disease.ELISA is an abbreviation for "enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay." In 1974, P. Perlmann and E. Engvall developed the test as a substitute for certain radioimmunoassay tests, and eventually, it replaced the western blot test for .
By testing the patient blood samples, the presence or absence of these antibodies can be measured using the ELISA. In the ELISA conducted for this lab, the antigen (from HIV virus) is adsorbed to the surface of the plastic . In this lab, students perform a virtual ELISA to test whether a particular antibody is present in a blood sample. Students engage in key science practices, including experimental design and data interpretation. The lab .What is an ELISA? The basic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), or enzyme immunoassay (EIA), is distinguished from other antibody-based assays because separation of specific and non-specific interactions occurs via serial binding to a solid surface, usually a polystyrene multiwell plate, and because quantitative results can be achieved.

ELISA, short for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a widely used laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample. It involves the binding of target molecules (antibodies or antigens) to a solid surface, followed by the addition of enzymes or fluorescent markers to generate a detectable signal. ELISA is .ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunoassay. It is a commonly used laboratory test to detect antibodies in the blood. An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful
test for knee meniscus tear
ELISA test results, what does a positive ELISA test tell you? ELISA results may be interpreted quantitatively, qualitatively or semi-quantitatively. In a quantitative assay, a serial dilution of a known standard is used to enable the generation of a standard curve, normally of optical density (OD) versus concentration. From this, the precise .The Parietal Cell Antibody, ELISA test contains 1 test with 1 biomarker.. Brief Description: The Parietal Cell Antibody, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) test is a medical laboratory examination that measures the presence of antibodies against parietal cells in the stomach. This test is crucial in diagnosing autoimmune conditions that affect the stomach lining and the .ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also often referred to as enzyme immunoassay (EIA). An ELISA, like other types of immunoassays, relies on antibodies to detect a target antigen using highly specific antibody-antigen interactions. In an ELISA assay, the antigen must be immobilized to a solid surface.A positive (reactive) ELISA for all samples must be used with a follow-up (confirmatory) test, such as the Western blot test, to make a positive diagnosis. Although false negative or false positive results are extremely rare, they may occur if the patient has not yet developed antibodies to HIV or if a mistake was made at the laboratory.
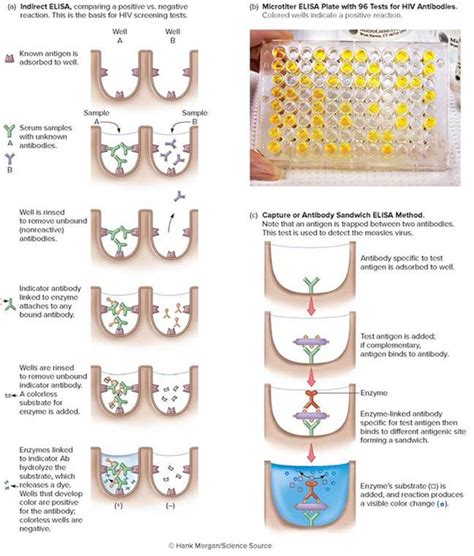
ELISA stands for 'enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay’, and ELISA tests are mainly used in research and clinical applications, including detecting viral infections such as hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In this article, we will outline the different types of ELISAs, explain how to analyze the assay data, .The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a powerful method for detecting and quantifying a specific protein in a complex mixture. Originally described by Engvall and Perlmann (1971), the method enables analysis of protein samples immobilized in microplate wells using specific antibodies. It is a commonly used laboratory test to detect antibodies in the blood. An antibody is a protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. ELISA is an effective and widely used technique in microbiology and virology—in particular, for investigating infectious pathogens. ELISA Principle
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay - or ELISA for short - is a laboratory technique or assay where antibodies or antigens in people’s samples are immobilized in a surface, and then detected by an antibody with an enzyme attached that causes a change of color.. So it’s useful to diagnose infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B, or malaria; and autoimmune diseases, like Graves’ .
The Interleukin-6, Highly Sensitive, ELISA test contains 1 test with 1 biomarker.. Brief Description: The Interleukin-6 (IL-6) test is a blood test that measures the level of IL-6, a cytokine, in the bloodstream. Cytokines are small proteins released by cells, particularly those in the immune system, which play crucial roles in cellular communication, inflammation, and the immune .
The ELISA Assay - The Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay, or ELISA, is a sensitive laboratory technique that uses antibodies to detect the presence of specific molecules (i.e. peptides, proteins, or hormones) in a complex sample. .
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is an immunological assay designed for detecting and quantifying soluble substances – such as peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones – in biological samples. In an ELISA, the antigen (target macromolecule) is immobilized on a microplate (usually a 96-well plate). This is then complexed with a specific antibody that is .
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional . ELISA: 1. Record results of Widal test using + or - signs: extremely agglutinated (+++) very agglutinated (++) . and hormones using antibodies and color changes. ELISA is a common medical and research lab technique. This page titled Lab 13: ELISA is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Nazzy Pakpour . The ELISA, or Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay, is an analytical biochemistry technique that uses antibodies to detect the presence of specific biomolecules.An example of a competition ELISA to test for antigen based on the direct detection method is shown in Figure 5 . Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate In this example the antigen concentration in the sample was low. The
Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a heterogeneous EIA technique used in clinical analyses. In this type of assay, one of the reaction components is nonspecifically adsorbed or .
Over the past three decades, ELISA or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, has become vital to many areas of research and has shown to have many applications—from detecting food and environmental contaminants to screening for HIV and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) antibodies ELISA overview. ELISA is a method used to quantitatively detect an antigen (i.e., toxin or foreign .ELISA is a plate-based assay that uses antibodies to specifically detect and quantify the amount of a target antigen in a liquid sample. . signal, compared to the standard control that is only in standard diluent. These issues are known matrix effects. To test if matrix effects are affecting an ELISA, a spike and recovery experiment can be . However, the technology is also built into some sophisticated laboratory equipment. In lateral flow tests (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)), fluids such as urine are applied to an absorbent pad on the test strip. . While not as quantitative as ELISA, these tests have the advantage of being fast, inexpensive, and not dependent on special equipment .
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunoassay. It is a commonly used laboratory test to detect antibodies in the blood. An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens.The presence of CCP antibodies, when considered in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical findings, is an aid in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Approximately 70% of RA patients are positive for anti-CCP IgG, while only 2% of .
Autoclave valves are complemented by a complete line of low pressure fittings, .
elisa test lab|elisa test explained